16.反射
1、引入
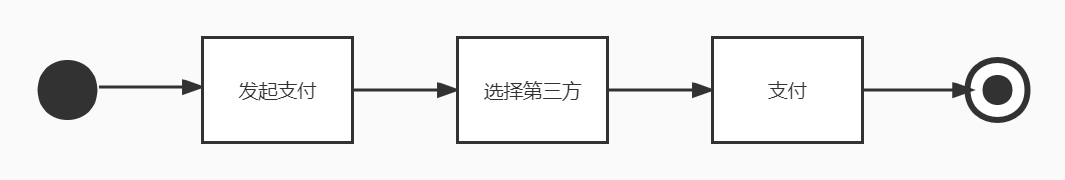
如图,我们简单地模拟用户点外卖的支付流程,由于第三方支付平台的不确定性,我们的整个支付流程就大有文章可做了。
创建类和接口
创建一个外卖接口
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
//接口的指定方:外卖
public interface MeiTuan {
//在线支付功能
void payOnline();
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
//接口的指定方:外卖
public interface MeiTuan {
//在线支付功能
void payOnline();
}
支付宝支付类
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
public class Alipay implements MeiTuan{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
System.out.println("支付宝支付");
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
public class Alipay implements MeiTuan{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
System.out.println("支付宝支付");
}
}
微信支付类
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
public class WeChat implements MeiTuan{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
System.out.println("微信支付");
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
public class WeChat implements MeiTuan{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
System.out.println("微信支付");
}
}
银行卡支付类
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
public class BankCard implements MeiTuan{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
System.out.println("银行卡支付");
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
public class BankCard implements MeiTuan{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
System.out.println("银行卡支付");
}
}
方式一:传统方式
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
/**
* 传统方式实现
*/
public class Test1_tradition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "微信";
if ("微信".equals(str)){
pay(new WeChat());
}
if ("支付宝".equals(str)){
pay(new Alipay());
}
if ("银行卡".equals(str)){
pay(new BankCard());
}
}
static void pay(WeChat weChat){
weChat.payOnline();
}
static void pay(Alipay alipay){
alipay.payOnline();
}
static void pay(BankCard bankCard){
bankCard.payOnline();
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
/**
* 传统方式实现
*/
public class Test1_tradition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "微信";
if ("微信".equals(str)){
pay(new WeChat());
}
if ("支付宝".equals(str)){
pay(new Alipay());
}
if ("银行卡".equals(str)){
pay(new BankCard());
}
}
static void pay(WeChat weChat){
weChat.payOnline();
}
static void pay(Alipay alipay){
alipay.payOnline();
}
static void pay(BankCard bankCard){
bankCard.payOnline();
}
}
方式二:多态
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
/**
* 利用多态提高扩展性
*/
public class Test2_polymorphism {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "微信";
if ("微信".equals(str)){
pay(new WeChat());
}
if ("支付宝".equals(str)){
pay(new Alipay());
}
if ("银行卡".equals(str)){
pay(new BankCard());
}
}
static void pay(MeiTuan meiTuan){
meiTuan.payOnline();
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
/**
* 利用多态提高扩展性
*/
public class Test2_polymorphism {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "微信";
if ("微信".equals(str)){
pay(new WeChat());
}
if ("支付宝".equals(str)){
pay(new Alipay());
}
if ("银行卡".equals(str)){
pay(new BankCard());
}
}
static void pay(MeiTuan meiTuan){
meiTuan.payOnline();
}
}
方式三:反射
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* 利用反射实现
*/
public class Test3_reflex {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str = "com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction.WeChat";
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(str);
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method method = cls.getMethod("payOnline");
method.invoke(o);
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* 利用反射实现
*/
public class Test3_reflex {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str = "com.chaodosen.demo.demo01_introduction.WeChat";
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(str);
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method method = cls.getMethod("payOnline");
method.invoke(o);
}
}
2、概念
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中:
- 对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;
- 对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;
- 这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
在编译后产生字节码文件的时候,类加载器子系统通过二进制字节流,负责从文件系统加载class文件。
在执行程序(java.exe)时候,将字节码文件读入JVM中,这个过程叫做类的加载。
然后在内存中对应创建一个java.lang.Class对象,这个对象会被放入字节码信息中,这个Class对象,就对应加载那个字节码信息,这个对将被作为程序访问方法区中的这个类的各种数据的外部接口。
所以:我们可以通过这个对象看到类的结构,这个对象就好像是一面镜子,透过镜子看到类的各种信息,我们形象的称之为反射这种“看透”class的能力
(theability of the program to examine itself)被称为introspection(内省、内观、反省)。Reflection和introspection是常被并提的两个术语。
说明:
- 在运行期间,如果我们要产生某个类的对象,Java虚拟机(JVM)会检查该类型的Class对象是否已被加载。
- 如果没有被加载,JVM会根据类的名称找到.class文件并加载它。
- 一旦某个类型的Class对象已被加载到内存,就可以用它来产生该类型的所有对象。
补充:
动态语言 vs 静态语言
1、动态语言
是一类在运行时可以改变其结构的语言:例如新的函数、对象、甚至代码可以被引进,已有的函数可以被删除或是其他结构上的变化。通俗点说就是在运行时代码
可以根据某些条件改变自身结构。主要动态语言: Object-C、 C#、JavaScript、 PHP、 Python、 Erlang 。
2、静态语言
与动态语言相对应的,运行时结构不可变的语言就是静态语言。如Java、C、C++。所以Java不是动态语言,但Java可以称之为“准动态语言”。即Java有一定的动态
性,我们可以利用反射机制、字节码操作获得类似动态语言的特性。Java的动态性让编程的时候更加灵活!
3、类加载与反射
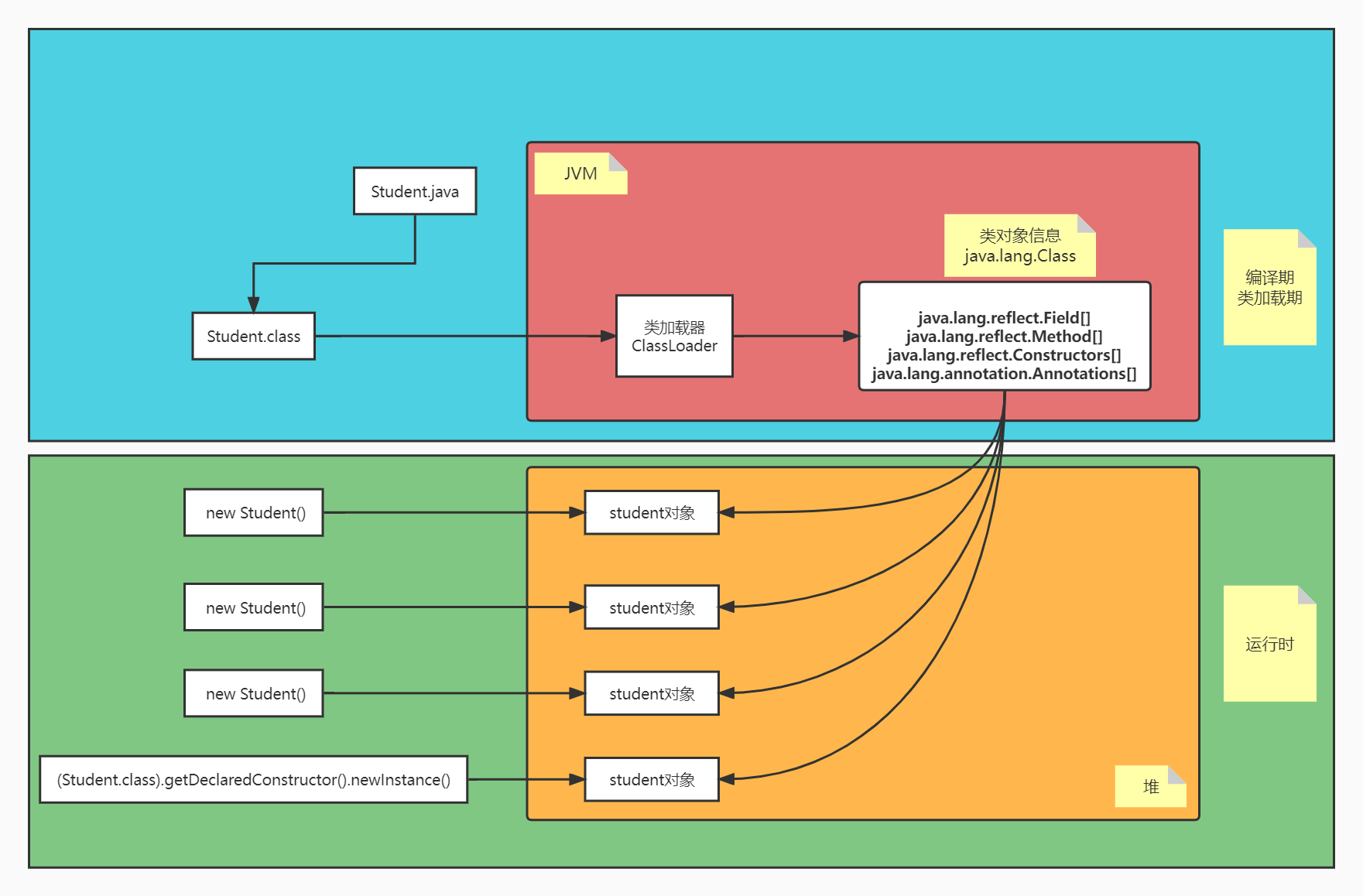
如图为Student类的加载过程:
- Student.java经过编译,得到Student.class字节码文件
- 经过类加载器在方法区中实例化一个Class对象
- 一个Class类(字节码文件)对应一个Class对象
- 该Class对象包含了Student类的基础信息:
- 属性
- 构造方法
- 方法
- 注解
- .....
有了这些基本信息(java.lang.Class对象),在运行期就可以根据这些信息来实例化Student类的对象
- new Student()
- (Student.class).getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance()
但是无论new 多少个Student对象,无论反射构建多少个Student对象,保存Student类信息的java.lang.Class对象都只有一个。
下面代码可以证明:
Class<?> cls1 = Class.forName("com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student");
Class<?> cls2 = Class.forName("com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student");
Class<? extends Student> cls3 = new Student().getClass();
Class<? extends Student> cls4 = new Student().getClass();
System.out.println(cls1==cls2);
System.out.println(cls2==cls3);
System.out.println(cls3==cls4);
Class<?> cls1 = Class.forName("com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student");
Class<?> cls2 = Class.forName("com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student");
Class<? extends Student> cls3 = new Student().getClass();
Class<? extends Student> cls4 = new Student().getClass();
System.out.println(cls1==cls2);
System.out.println(cls2==cls3);
System.out.println(cls3==cls4);
以上结果均为true
4、操作反射的Java类
Person类
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation;
import java.io.Serializable;
//作为一个父类
public class Person implements Serializable {
//属性
private int age;
public String name;
//方法
private void eat(){
System.out.println("Person.eat");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("Person.sleep");
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation;
import java.io.Serializable;
//作为一个父类
public class Person implements Serializable {
//属性
private int age;
public String name;
//方法
private void eat(){
System.out.println("Person.eat");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("Person.sleep");
}
}
Student类
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation;
//Student作为子类
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello Student")
public class Student extends Person implements MyInterface{
//属性
private int sno;
double height;
protected double weight;
public double score;
//方法
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello showInfo")
public String showInfo(){
return "I'm a good student";
}
public String showInfo(int a,int b){
return "overload -> I'm a good student";
}
private void work(int a){
System.out.println("I want to be a coder");
}
void happy(){
System.out.println("wish u happy everyday");
}
protected int getSno(){
return sno;
}
public static void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
//构造器
public Student(){
System.out.println("NoConstructor");
}
public Student(double weight,double height){
this.weight = weight;
this.height = height;
}
private Student(int sno){
this.sno = sno;
}
Student(int sno,double weight){
this.sno = sno;
this.weight = weight;
}
protected Student(int sno,double weight,double height){
this.sno = sno;
this.weight = weight;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello myMethod")
public void myMethod() throws RuntimeException{
System.out.println("override myMethod()");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sno=" + sno +
", height=" + height +
", weight=" + weight +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation;
//Student作为子类
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello Student")
public class Student extends Person implements MyInterface{
//属性
private int sno;
double height;
protected double weight;
public double score;
//方法
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello showInfo")
public String showInfo(){
return "I'm a good student";
}
public String showInfo(int a,int b){
return "overload -> I'm a good student";
}
private void work(int a){
System.out.println("I want to be a coder");
}
void happy(){
System.out.println("wish u happy everyday");
}
protected int getSno(){
return sno;
}
public static void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
//构造器
public Student(){
System.out.println("NoConstructor");
}
public Student(double weight,double height){
this.weight = weight;
this.height = height;
}
private Student(int sno){
this.sno = sno;
}
Student(int sno,double weight){
this.sno = sno;
this.weight = weight;
}
protected Student(int sno,double weight,double height){
this.sno = sno;
this.weight = weight;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello myMethod")
public void myMethod() throws RuntimeException{
System.out.println("override myMethod()");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sno=" + sno +
", height=" + height +
", weight=" + weight +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
自定义接口MyInterface
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation;
public interface MyInterface {
void myMethod();
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation;
public interface MyInterface {
void myMethod();
}
自定义注解MyAnnotation
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE;
/*
@Target: 定义当前注解能够修饰程序中的哪些元素
@Retention: 定义注解的生命周期
*/
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE;
/*
@Target: 定义当前注解能够修饰程序中的哪些元素
@Retention: 定义注解的生命周期
*/
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();
}
4.1、获取字节码的四种方式
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo03_get_bytecode_info;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Person;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//以Person的字节码信息为例
// 1、通过getClass()获取
Person person = new Person();
Class<? extends Person> class1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(class1);
// 2、通过内置class属性
Class<Person> class2 = Person.class;
System.out.println(class2);
System.out.println(class1==class2);
// 3、调用Class类提供的静态方法forName
Class<?> class3 = Class.forName("com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Person");
System.out.println(class3);
// 4、通过当前类拿到类加载器,用类加载器获取对应的字节码对象
ClassLoader classLoader = Test.class.getClassLoader();
Class<?> class4 = classLoader.loadClass("com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Person");
System.out.println(class4);
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo03_get_bytecode_info;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Person;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//以Person的字节码信息为例
// 1、通过getClass()获取
Person person = new Person();
Class<? extends Person> class1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(class1);
// 2、通过内置class属性
Class<Person> class2 = Person.class;
System.out.println(class2);
System.out.println(class1==class2);
// 3、调用Class类提供的静态方法forName
Class<?> class3 = Class.forName("com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Person");
System.out.println(class3);
// 4、通过当前类拿到类加载器,用类加载器获取对应的字节码对象
ClassLoader classLoader = Test.class.getClassLoader();
Class<?> class4 = classLoader.loadClass("com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Person");
System.out.println(class4);
}
}
其中第三种是最常用的获取Class对象的方法,因为字符串传参增强了配置的灵活性
4.2、可以作为Class对象的种类
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo04_instances_of_class;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Person;
/*
Class类的具体的实例:
1、类:内部类、外部类
2、接口
3、注解
4、数组
5、基本数据类型
6、void
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<Person> class1 = Person.class;
Class<Comparable> class2 = Comparable.class;
Class<Override> class3 = Override.class;
int[] arr1 = {1,2,3};
Class<? extends int[]> class4 = arr1.getClass();
int[] arr2 = {5,6,7};
Class<? extends int[]> class5 = arr2.getClass();
System.out.println(class4==class5);//相同维度和数据类型得到的字节码是同一个
Class<Integer> class6 = int.class;
System.out.println(class6);
Class<Void> class7 = void.class;
System.out.println(class7);
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo04_instances_of_class;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Person;
/*
Class类的具体的实例:
1、类:内部类、外部类
2、接口
3、注解
4、数组
5、基本数据类型
6、void
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<Person> class1 = Person.class;
Class<Comparable> class2 = Comparable.class;
Class<Override> class3 = Override.class;
int[] arr1 = {1,2,3};
Class<? extends int[]> class4 = arr1.getClass();
int[] arr2 = {5,6,7};
Class<? extends int[]> class5 = arr2.getClass();
System.out.println(class4==class5);//相同维度和数据类型得到的字节码是同一个
Class<Integer> class6 = int.class;
System.out.println(class6);
Class<Void> class7 = void.class;
System.out.println(class7);
}
}
4.3、获取构造器并创建对象
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo05_operator;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class GetConstructor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取字节码信息
Class<Student> class1 = Student.class;
//通过字节码信息可以获取的构造器
//getConstructors()只能获取当前运行时类中被public修饰的构造器
Constructor<?>[] c1 = class1.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> c : c1) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------");
//getDeclaredConstructors() 可以获取运行时类的全部构造器
Constructor<?>[] c2 = class1.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> c : c2) {
System.out.println(c);
}
Student student = class1.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取指定的构造器
//获取空的构造器
Constructor<Student> c3 = class1.getConstructor();
System.out.println(c3);
//得到两个参数的有参构造器
Constructor<Student> c4 = class1.getConstructor(double.class, double.class);
System.out.println(c4);
//得到一个参数的构造器且是private修饰的
Constructor<Student> c5 = class1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);
System.out.println(c5);
//有了构造器之后就可以创建对象
Student student1 = c3.newInstance();
System.out.println(student1);
Student student2 = c4.newInstance(180.5, 120.6);
System.out.println(student2);
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo05_operator;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class GetConstructor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取字节码信息
Class<Student> class1 = Student.class;
//通过字节码信息可以获取的构造器
//getConstructors()只能获取当前运行时类中被public修饰的构造器
Constructor<?>[] c1 = class1.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> c : c1) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------");
//getDeclaredConstructors() 可以获取运行时类的全部构造器
Constructor<?>[] c2 = class1.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> c : c2) {
System.out.println(c);
}
Student student = class1.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取指定的构造器
//获取空的构造器
Constructor<Student> c3 = class1.getConstructor();
System.out.println(c3);
//得到两个参数的有参构造器
Constructor<Student> c4 = class1.getConstructor(double.class, double.class);
System.out.println(c4);
//得到一个参数的构造器且是private修饰的
Constructor<Student> c5 = class1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);
System.out.println(c5);
//有了构造器之后就可以创建对象
Student student1 = c3.newInstance();
System.out.println(student1);
Student student2 = c4.newInstance(180.5, 120.6);
System.out.println(student2);
}
}
4.4、获取属性并赋值
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo05_operator;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class GetField {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//获取字节码信息
Class<Student> cls = Student.class;
//获取属性
//getFields()获取当前运行时类和父类中被public修饰的方法
Field[] f1 = cls.getFields();
for (Field field : f1) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------");
//getDeclaredFields()获取运行时类中的所有属性
Field[] f2 = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : f2) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取指定的属性
Field name = cls.getField("name");
System.out.println(name);
Field sno = cls.getDeclaredField("sno");
System.out.println(sno);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取属性的具体结构
//修饰符
int modifiers = sno.getModifiers();
System.out.println(modifiers);
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(modifiers));
//数据类型
Class<?> type = sno.getType();
System.out.println(type);
//属性名
String s = sno.getName();
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------");
//给属性赋值 :前提必须要有对象
Field score = cls.getField("score");
Student student = cls.newInstance();
score.set(student,98.0);
System.out.println(student);
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo05_operator;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class GetField {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//获取字节码信息
Class<Student> cls = Student.class;
//获取属性
//getFields()获取当前运行时类和父类中被public修饰的方法
Field[] f1 = cls.getFields();
for (Field field : f1) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------");
//getDeclaredFields()获取运行时类中的所有属性
Field[] f2 = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : f2) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取指定的属性
Field name = cls.getField("name");
System.out.println(name);
Field sno = cls.getDeclaredField("sno");
System.out.println(sno);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取属性的具体结构
//修饰符
int modifiers = sno.getModifiers();
System.out.println(modifiers);
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(modifiers));
//数据类型
Class<?> type = sno.getType();
System.out.println(type);
//属性名
String s = sno.getName();
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------");
//给属性赋值 :前提必须要有对象
Field score = cls.getField("score");
Student student = cls.newInstance();
score.set(student,98.0);
System.out.println(student);
}
}
4.5、获取方法并调用
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo05_operator;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class GetMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//获取字节码信息
Class<Student> cls = Student.class;
//获取方法
//getMethods() 获取运行时类和所有父类中被public修饰的方法
Method[] m1 = cls.getMethods();
for (Method method : m1) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------");
//getDeclaredMethods()获取运行时类中的所有方法
Method[] m2 = cls.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : m2) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取指定的方法
Method m3 = cls.getMethod("showInfo");
System.out.println(m3);
Method m4 = cls.getMethod("showInfo", int.class,int.class);
System.out.println(m4);
System.out.println("*---------------------------------------------------------------------");
Method work = cls.getDeclaredMethod("work",int.class);
System.out.println(work);
//获取方法的具体结构
//修饰符
int modifiers = work.getModifiers();
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(modifiers));
//返回值
Class<?> type = work.getReturnType();
System.out.println(type);
//方法名
String name = work.getName();
System.out.println(name);
//参数列表
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = work.getParameterTypes();
for (Class<?> parameterType : parameterTypes) {
System.out.println(parameterType);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取注解
Method myMethod = cls.getMethod("myMethod");
Annotation[] annotations = myMethod.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------");
//获取异常
Class<?>[] exceptionTypes = myMethod.getExceptionTypes();
for (Class<?> exceptionType : exceptionTypes) {
System.out.println(exceptionType);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------");
//调用方法
Student student = cls.newInstance();
myMethod.invoke(student);
Object o = m4.invoke(student, 1, 2);
System.out.println(o);
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo05_operator;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class GetMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//获取字节码信息
Class<Student> cls = Student.class;
//获取方法
//getMethods() 获取运行时类和所有父类中被public修饰的方法
Method[] m1 = cls.getMethods();
for (Method method : m1) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------");
//getDeclaredMethods()获取运行时类中的所有方法
Method[] m2 = cls.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : m2) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取指定的方法
Method m3 = cls.getMethod("showInfo");
System.out.println(m3);
Method m4 = cls.getMethod("showInfo", int.class,int.class);
System.out.println(m4);
System.out.println("*---------------------------------------------------------------------");
Method work = cls.getDeclaredMethod("work",int.class);
System.out.println(work);
//获取方法的具体结构
//修饰符
int modifiers = work.getModifiers();
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(modifiers));
//返回值
Class<?> type = work.getReturnType();
System.out.println(type);
//方法名
String name = work.getName();
System.out.println(name);
//参数列表
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = work.getParameterTypes();
for (Class<?> parameterType : parameterTypes) {
System.out.println(parameterType);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------");
//获取注解
Method myMethod = cls.getMethod("myMethod");
Annotation[] annotations = myMethod.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------");
//获取异常
Class<?>[] exceptionTypes = myMethod.getExceptionTypes();
for (Class<?> exceptionType : exceptionTypes) {
System.out.println(exceptionType);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------");
//调用方法
Student student = cls.newInstance();
myMethod.invoke(student);
Object o = m4.invoke(student, 1, 2);
System.out.println(o);
}
}
4.6、获取类的接口、所在包、注解
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo05_operator;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
public class GetClassInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取字节码信息
Class<Student> cls = Student.class;
//获取接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = cls.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> anInterface : interfaces) {
System.out.println(anInterface);
}
Class<? super Student> superclass = cls.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] interfaces1 = superclass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> aClass : interfaces1) {
System.out.println(aClass);
}
//获取运行时类所在的包
Package aPackage = cls.getPackage();
System.out.println(aPackage);
System.out.println(aPackage.getName());
Annotation[] annotations = cls.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation );
}
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo05_operator;
import com.chaodosen.demo.demo02_preparation.Student;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
public class GetClassInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取字节码信息
Class<Student> cls = Student.class;
//获取接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = cls.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> anInterface : interfaces) {
System.out.println(anInterface);
}
Class<? super Student> superclass = cls.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] interfaces1 = superclass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> aClass : interfaces1) {
System.out.println(aClass);
}
//获取运行时类所在的包
Package aPackage = cls.getPackage();
System.out.println(aPackage);
System.out.println(aPackage.getName());
Annotation[] annotations = cls.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation );
}
}
}
5、应用场景
5.1、通过配置信息调用类的方法
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Extend {
public void invokeClassMethod(String className,
String methodName,
Object ... args)
throws ClassNotFoundException,
InstantiationException,
IllegalAccessException,
NoSuchMethodException,
InvocationTargetException {
//获取字节码信息
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className);
//创建对象(对象实例化)
Object o = cls.newInstance();
//获取并调用方法
Method method = cls.getMethod(methodName);
method.invoke(o,args);
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Extend {
public void invokeClassMethod(String className,
String methodName,
Object ... args)
throws ClassNotFoundException,
InstantiationException,
IllegalAccessException,
NoSuchMethodException,
InvocationTargetException {
//获取字节码信息
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className);
//创建对象(对象实例化)
Object o = cls.newInstance();
//获取并调用方法
Method method = cls.getMethod(methodName);
method.invoke(o,args);
}
}
5.2、结合注解特殊使用
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TableName {
String name();
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TableName {
String name();
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend;
@TableName(name = "student")
public class Student {
public String name;
private int age;
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend;
@TableName(name = "student")
public class Student {
public String name;
private int age;
}
<dependency>
<groupId>org.reflections</groupId>
<artifactId>reflections</artifactId>
<version>0.10.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.reflections</groupId>
<artifactId>reflections</artifactId>
<version>0.10.2</version>
</dependency>
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend;
import org.reflections.Reflections;
import java.util.Set;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String packageName = "com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend";
Reflections reflections = new Reflections(packageName);
Set<Class<?>> set = reflections.getTypesAnnotatedWith(TableName.class);
for (Class<?> cls : set) {
TableName tableName = cls.getAnnotation(TableName.class);
System.out.println(tableName.name());
}
}
}
package com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend;
import org.reflections.Reflections;
import java.util.Set;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String packageName = "com.chaodosen.demo.demo06_extend";
Reflections reflections = new Reflections(packageName);
Set<Class<?>> set = reflections.getTypesAnnotatedWith(TableName.class);
for (Class<?> cls : set) {
TableName tableName = cls.getAnnotation(TableName.class);
System.out.println(tableName.name());
}
}
}
待做:构建MybatisPlus
6、优缺点
- 优点:
- 自由,使用灵活,不受类的访问权限限制。
- 可以根根据类名、方法名来调用方法、使很多业务实现可以灵活配置
- 缺点
- 正由于反射不受类的访问权限的限制,导致了安全性低
- 相对于正常的创建对象调用访问,反射由于存在类和方法的实例化过程,性能相对也较低
- 破坏了java类的封装性、类的信息隐藏性和边界被破坏
 知识星球
知识星球